_
|
||||||||
|
High
Conformation sensitive capillary electrophoresis (CSCE)
|
||||||||
|
Project leader: Chris Mattocks Download
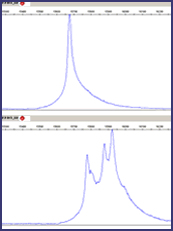
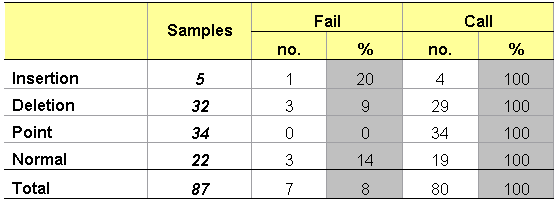
Application Note in pdf format (1.02 MB) CSCE is essentially fluorescent heteroduplex analysis (technical description). We are currently evaluating a method developed and validated by the Cancer Genome group at the Sanger Centre. The fragment of interest is amplified by SPODS-PCR using one fluorescently labelled universal primer. The PCR products are then heteroduplexed by heating to 95°C and cooling to room temperature over a period of 40 minutes. Up to four differently labelled products can be mixed and a final dilution of 1:120 of the original PCR product is made before adding a LIZ size standard and running on the ABI 3730 – 48 capillary sequence analyser. Fragments are separated according to size and conformation adopted as a result of any mismatched base pairs. Currently analysis is carried out by overlaying test trace with wild-type using the ABI GeneMapper software. A peak threshold has been defined below which the analysis is failed. We will be investigating the possibility of further automation of the analysis. Although, ideally, mutations should generate four distinct peaks (homozygous wild-type, homozygous mutant, 2x heterozygous mutant), in practice two or three is more usual (CSCE examples). The table below summarises a pilot study involving a single 96 well plate of samples comprising fragments from six different amplicons of BRCA1 exon 11. This pilot was carried out using manual liquid handling and no multiplexing for analysis. A more extensive validation is being set up in the context of the full automated high throughput pipeline.
|
||||||||
Last Updated: 6 August, 2008 by G. Watkins. |